In this article
Imagine this, your team has implemented multi-factor authentication, strengthened endpoints with XDR and fine tuned firewall policies and one morning an alert pops up and says a sophisticated cyber attack has snuck past those defences. In such moments, a company or enterprise can face threats that put the very life of the business at risk, with the potential for significant loss.
At TechBrain we don’t see cyber insurance as an afterthought or a mere financial formality. We see it as a fundamental pillar that complements our managed security services.
While our SOC analysts and XDR engines are working 24/7 to detect and contain threats before they spread, a well crafted insurance policy is ready to cover the financial consequences that lie beyond technical recovery—legal services, regulatory notifications, reputational management, confidential data liability, third party claims and business operations losses.
For IT managers juggling competing priorities and business leaders balancing budgets and liabilities, it is crucial for any company or enterprise to protect the life of their business and minimize loss. This dual approach gives you agility and assurance. A layered defence means you’re actively reducing risk, and risk transfer means you won’t be left holding the bill if an incident still gets through.
In the sections that follow we’ll walk through how cyber liability insurance works with our managed services, outline the critical controls underwriters demand and explain how to integrate these elements into a cohesive, resilient cyber strategy that complements your current business insurance.
Cyber Liability Insurance and Cyber Extortion
Cyber liability insurance or cyber security insurance is a specific policy that transfers the financial risk of certain cyber events. Unlike business cover or property insurance, cyber liability coverage is designed to cover losses from digital incidents, and the insurance cover defines the scope of protection against risks such as data destruction, hacking, and extortion.
A cyber insurance policy covers a range of risks including data breaches, hacking, extortion and legal expenses. Its main purpose is to reduce the financial impact of cybercrime by paying out organisations for:
- Incident Response Costs: Forensic investigations, legal fees and PR can cost tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars. Certain expenses, such as notification and reputation management, are included in the policy benefits.
- Data Recovery & Restoration: Costs to recover or rebuild compromised systems and data.
- Business Interruption (BI): Lost revenue and extra expenses when critical systems are down.
- Ransom & Extortion: Payments to the bad guys (subject to insurer approval) and costs to negotiate with them.
- Regulatory Fines & Investigation Costs: Under Australia’s Notifiable Data Breaches (NDB) scheme enforced by the Office of the Australian Information Commissioner (OAIC) organisations must notify if personal information is compromised. Non-compliance can result in fines up to $2.22 million for a body corporate.
- Third-Party Liabilities: Legal defence costs, settlements and judgments if customers, partners or other stakeholders sue you because of cyber security breach, especially if the breach results in data theft. Companies can be held liable for damages resulting from compromised data, and cyber insurance helps manage this liability.
A typical cyber insurance claim will have costs such as forensic investigation, legal fees and customer notification expenses.
No matter how good your cyber security is no defence is impenetrable. Human error, zero-day vulnerabilities or state sponsored attacks can bypass controls.
Cyber insurance is essential for organisations facing breach liability. It covers response and recovery costs and helps mitigate financial and reputational fallout that prevention alone can’t avoid.
First Party vs. Third Party
Cyber liability policies break down into two main areas.
First Party
- Forensics & Legal: Investigation and legal fees.
- Business Interruption: Lost income when key systems are down.
- Crisis Management: PR resources for reputational and customer notifications.
Third Party
- Privacy Liability: Defence costs and settlements if personal data is exposed.
- Network Security Liability: If your network is used to attack a third party.
- Regulatory Proceedings & Fines: Legal costs and fines under the Privacy Act 1988 (if insurable by law).
Set your policy limits based on what you actually stand to lose. First-party cover pays for direct costs like forensics, legal fees, business-interruption losses and crisis management, while third-party cover protects you if customers or regulators take legal action over exposed data or network misuse.
Even with robust security controls, the financial and reputational impact of a single breach can far exceed your premium, so tailor both first-party and third-party limits to your unique risk profile and regulatory requirements.

How Managed Security Services Fuel Insurance
Cyber insurance is reactive, it comes into play after an incident to cover financial losses.
But cyber insurance should not replace robust cyber defence and risk management strategies; it’s meant to complement them. Managed security services are proactive, they aim to prevent or limit the impact of incidents. Today’s insurers demand proof of proactive controls before they will underwrite a policy at competitive rates — or, in some cases, at all.
Buying a policy without strong security can be too expensive, have restrictive sub-limits or be declined outright. Ongoing care in maintaining and managing your security systems and protocols is essential to reduce risks and get the most out of your cyber insurance policy. As part of a comprehensive risk management and incident response plan, hiring cyber security professionals is highly valuable to ensure your organisation is prepared to prevent and manage cyber threats.
At TechBrain our managed services address the key underwriting requirements, demonstrating to underwriters that your organisation is committed to good cyber hygiene. Let’s look at how each managed service maps to insurer demands.
Reducing Claim Frequency & Cost
Each managed service meets an underwriting requirement and reduces the frequency and cost of claims:
- Faster Detection & Response: 24/7 SOC and XDR means breaches are detected in minutes not days. Containment limits data exfiltration, BI duration and remediation costs.
- Reliable Data Recovery: Immutable, tested backups eliminate the need for ransom payments. Hackers are making unauthorised demands and causing disruption through cyber attacks but with reliable backups you can restore from a clean backup and avoid paying criminals.
- Consistent Patch Management: Addressing critical vulnerabilities promptly reduces your attack surface. Attackers have fewer entry points to exploit, reducing the chance of a successful penetration.
- Human Risk Mitigation: Phishing resistant users means fewer compromised credentials. This reduces the risk of spear phishing driven ransomware or BEC attacks which are the costliest claims.
Simplifying the Claims Process
If an incident occurs managed services provide critical support to expedite the claims process:
- Centralised Logs for Forensics: A SOC with retained SIEM logs provides investigators with the data to understand breach scope and root cause. Well maintained logs reduce forensic billable hours.
- Documented Incident Response Playbooks: We maintain clear runbooks that outline responsibilities, technical steps and communication workflows during a breach. These align with insurer requirements to engage panel vendors and get prior approval for expenses.
- Coordinated Expert Response: We work with your chosen cyber broker to facilitate a seamless handover to insurer approved forensics, legal and PR firms. Quick coordination means you meet policy SLA deadlines (e.g. notify insurers within 24 hours of detection).
The Virtuous Cycle: Strong managed security → Better insurability & premiums → Lower claim frequency/severity → Easier claims support → Business resilience.
The Underwriter’s Checklist: Passing the Cyber Insurance Application
When applying for cyber insurance cover you will go through a thorough underwriting process. Underwriters may have different requirements and risk assessments for different industries, so organisations should be aware of industry-specific risks when applying for coverage.
Underwriters will ask you detailed questions about your cyber security posture. Below is a checklist of the key areas they will verify and how your MSP like TechBrain can help you meet each requirement.
Multi-Factor Authentication Everywhere
Insurer Question: “Have you implemented MFA for all administrative accounts, remote access (VPN/VDI), critical servers and cloud applications?”
MSP Role:
- We implement MFA on all high risk access points.
- Maintain an MFA inventory dashboard.
- Provide quarterly MFA enforcement rates (target 100%).
Advanced Endpoint Protection (EDR/XDR)
Insurer Question: “Do you have EDR/XDR agents deployed on all endpoints (workstations, servers, laptops) and continuously monitored by a SOC?”
MSP Role:
- Deploy and maintain EDR/XDR agents across all endpoints.
- Tune detection rules to minimize false positives.
- Share EDR/XDR health metrics and detection logs as part of your quarterly security report.
24/7 Monitoring & Detection (SOC/MDR)
Insurer Question: “Is your network and endpoint telemetry ingested into a SIEM or XDR platform and actively monitored by a qualified SOC team?”
MSP Role:
- Provide 24/7 SOC/MDR with real-time alerting.
- Document escalation procedures, including on-call schedules and SLA response times (e.g. acknowledge critical alerts within 15 minutes).
- Issue quarterly SOC performance metrics (MTD, MTR).
Robust, Tested Backups
Insurer Question: “Describe your backup strategy. Are backups immutable/offline? How frequently do you test restores?”
MSP Role:
- Design and manage a 3-2-1 backup architecture (three copies, two media types, one offsite).
- Conduct quarterly restore simulations and document success/failure results.
- Provide backup health reports showing zero backup failures in the past 90 days.
Patching Cadence & Vulnerability Management
Insurer Question: “What is your process for identifying and remediating critical vulnerabilities? Are patches deployed within 30 days?”
MSP Role:
- Perform weekly vulnerability scans with CVSS scoring.
- Deploy critical patches within 14 days; high-risk patches within 7 days.
- Maintain a patch-tracking dashboard and include audit reports in your insurance submission.
Incident Response Plan Documented & Tested
Insurer Question: “Do you have a documented cyber disaster recovery plan? When was it last tested?”
MSP Role:
- Develop and maintain an IR playbook aligned with ACSC guidelines (e.g., detection, containment, eradication, recovery, lessons learned), ensuring incidents are managed end-to-end for comprehensive coverage from detection to recovery.
- Facilitate biannual tabletop exercises simulating ransomware attacks, BEC and data breach scenarios.
- Document exercise outcomes, action items and improvements implemented.
Employee Training & Phishing Simulations
Insurer Question: “Do you conduct regular security awareness training and phishing simulations for your employees? What are your employees’ click/compromise rates?”
MSP Role:
- Emphasize the importance of employees in maintaining a strong security posture by ensuring all employees receive regular security awareness training.
- Deploy a quarterly phishing campaign targeting high-risk departments.
- Provide quarterly click-rate metrics for employees (target: < 5%).
- Offer refresher training modules for employees who fall for simulated phishing. Employee awareness and training are critical components of reducing cyber risk and lowering insurance costs.
Network Segmentation & Access Control
Insurer Question: “Is your internal network segmented to limit lateral movement? How is access to sensitive systems controlled?”
MSP Role:
- Implement VLAN segmentation, zero-trust principles and least-privilege access.
- Configure network ACLs and next-generation firewalls to restrict east-west traffic.
- Provide network architecture diagrams and access control lists (ACL) as part of your underwriting submission.
By working with an MSP like TechBrain you’re not just ticking boxes; you’re building a demonstrably mature security posture. This reduces underwriting friction, shortens negotiation cycles and often results in better premiums and terms.
Reading the Fine Print: Beyond the Basics
Even after you’ve got a cyber insurance policy in-place it’s important to read the fine print with your cyber broker and your MSP/IT team. Key areas to review include:
Coverage Limits & Sub-Limits:
- Ransom payments often have sub-limits (e.g. AUD 500,000). If your ransom is likely to be more than that you may need a separate ransomware response endorsement.
- Business interruption limits may be different for bespoke services versus standard operation.
Excesses/Retentions:
- Typical excesses start at AUD 10,000–20,000. Higher excesses can reduce premiums but increase out-of-pocket costs during a claim.
Key Exclusions:
- Prior Acts: Incidents known but not reported before policy inception.
- Known/Unpatched Vulnerabilities: If you don’t patch a critical CVE within the insurer’s time frame (e.g., 30 days), related incidents may be excluded.
- Infrastructure Failure: Some policies exclude losses caused by hardware or software failures unrelated to malicious attacks.
- Acts of War/Terrorism: Coverage for state-sponsored attacks may require a separate endorsement.
- Bodily Injury & Property Damage: Cyber policies often exclude physical harm or tangible property damage. If your environment floats into OT (operational technology), you may need a combined E&O + cyber policy.
Claims Processes & Vendor Panels:
- Policies generally require insurer consent before you engage third-party forensics, legal or PR firms.
- Some insurers restrict you to their panel vendors; if you prefer a different firm, you may have to cover the cost difference.
- There are often strict reporting timeframes (e.g., notify within 24–48 hours of discovery) to avoid coverage denial.
Your MSP’s documentation logs, incident reports, patch records and tabletop exercise summaries plays a vital role in demonstrating compliance with policy conditions. Failing to maintain required controls or missing reporting deadlines can jeopardise coverage, so treat these policy nuances seriously.
Cyber Insurance Cost
Cyber insurance premiums in Australia vary by business size, industry and security maturity. While the upfront cost may seem high, it’s a small price to pay compared to the average cost of a breach.
Here are some broad averages to consider but please do check with your insurance broker based on your individual circumstances:
- Small-to-Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
- Basic coverage: $1,000–$2,000 per year.
- Varies by turnover, existing controls and industry.
- Medium-Sized Organisations
- Typical premiums: $5,000–$10,000 per year.
- Increases if turnover is over $50 million or if security controls are not fully mature.
- High-Risk Sectors (Finance, Healthcare, Retail)
- Premiums start at $10,000–$20,000 or more per year.
- Higher rates due to regulated data, stricter compliance requirements and historical claim frequency.
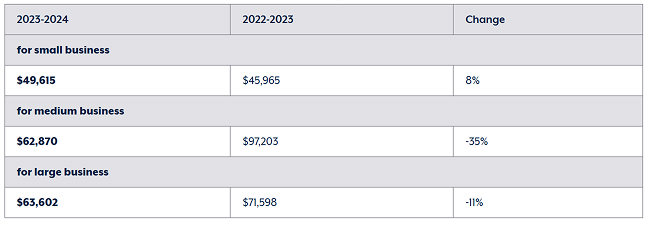
According to the Australian Cyber Security Centre’s 2023–24 report, small businesses experience an average cost of $49,600 per cyber incident, medium businesses $62,800 and large businesses $63,600 per reported breach.
Cyber Resilience is an Ongoing Journey
Cyber resilience is not a one-off project but a continuous process. By integrating managed security services with cyber insurance you get a holistic risk management framework:
- Proactive Defence Drives Insurability: A mature security posture 24/7 monitoring, rapid patching, regular testing—reduces both frequency and severity of incidents. Insurers reward this with lower premiums and fewer sub-limits.
- Insurance Enables Rapid Recovery: When an incident occurs insurance ensures your financial stability. This allows your technical teams to focus on remediation not cash flow.
- Continuous Improvement Loop: Post-incident reviews generate lessons learned. Your MSP updates controls, refines playbooks and shares with underwriters, leading to better terms at renewal.
- Regulatory Compliance & Stakeholder Confidence: Meeting APS CPS 234 (for financial institutions) or ACSC Essential Eight maturity not only satisfies insurers but also regulators and customers. Demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements gives you trust across the board.
As a trusted MSP, TechBrain’s role is to help you through each stage: from initial risk assessments to ongoing control implementation, from insurance application support to incident response coordination.
This partnership means you’re prepared for the “when,” not the “if,” of a cyber incident.
Get Ready for the Future: Act Now
True cyber resilience means aligning security tooling, processes and financial safeguards, here’s how to get started:
Check Your Security Against the Underwriter’s Checklist
-
- Review MFA coverage, EDR/XDR deployment, SOC monitoring, backup resilience and patch cadence.
- Identify gaps, your MSP can prioritise these based on risk level and insurer requirements.
Engage TechBrain for a Holistic Cyber Risk Assessment
-
- We’ll map your critical assets, quantify business interruption impact and highlight areas for improvement.
- With these findings you can approach brokers with confidence and get competitive policy terms.
Talk to a Cyber Insurance Specialist
-
- Share your improved security metrics and documentation (vulnerability scan reports, SOC performance dashboards, IR playbooks).
- Work together to set policy limits and sub-limits that match your actual risk.
Align Your Plans
-
- Security Plan: Implement key controls (e.g., full EDR, network segmentation, PSIRT processes).
- Insurance Plan: Schedule policy reviews to align with control maturity (e.g., 90% patch compliance by Q3).
Use TechBrain’s Managed Cyber Services for Proactive Defence
-
- Build a solid security foundation with our Managed Security Service.
- Get 24/7 threat detection with our Managed SOC Service.
- Implement insurer required endpoint protection with our Managed XDR Service.
Cyber threats are constantly evolving. Combining managed security with cyber insurance cover gives you a robust shield for your business.
Partner with TechBrain as your MSP and a specialist cyber broker and you’ll turn uncertainty into confidence so if and when a breach occurs you’re ready technically and financially to respond quickly and maintain stakeholder trust.
Please note, TechBrain is not a cyber broker, the above is not intended as advice and is general in nature. Please engage your specialist cyber broker who will consider your specific circumstances and can advise you accordingly.